How To Repair Air Suspension Compressor
My recent conclusion, to proactively fix a modest leak on my PTT, turned into a total air suspension debug session.
I learned many useful details, which I promise you tin keep in mind, when your machine starts exhibiting air interruption issues.
Troubleshooting the air suspension is not super difficult, but information technology actually helps to sympathise all components, and how they work together to keep the Panamera performing at its peak.
Terms below and ordering mostly lucifer terminology in the FSM, to help reduce ambivalence.
Start – overview of the entire air suspension.
Expect over the entire diagram and identify each of the components shown, so you can get a skilful experience for where each part is, how it connects to the rest of the system, and how the unabridged organization is supposed to work equally a unit.
PANAMERA AIR SUSPENSION COMPONENTS 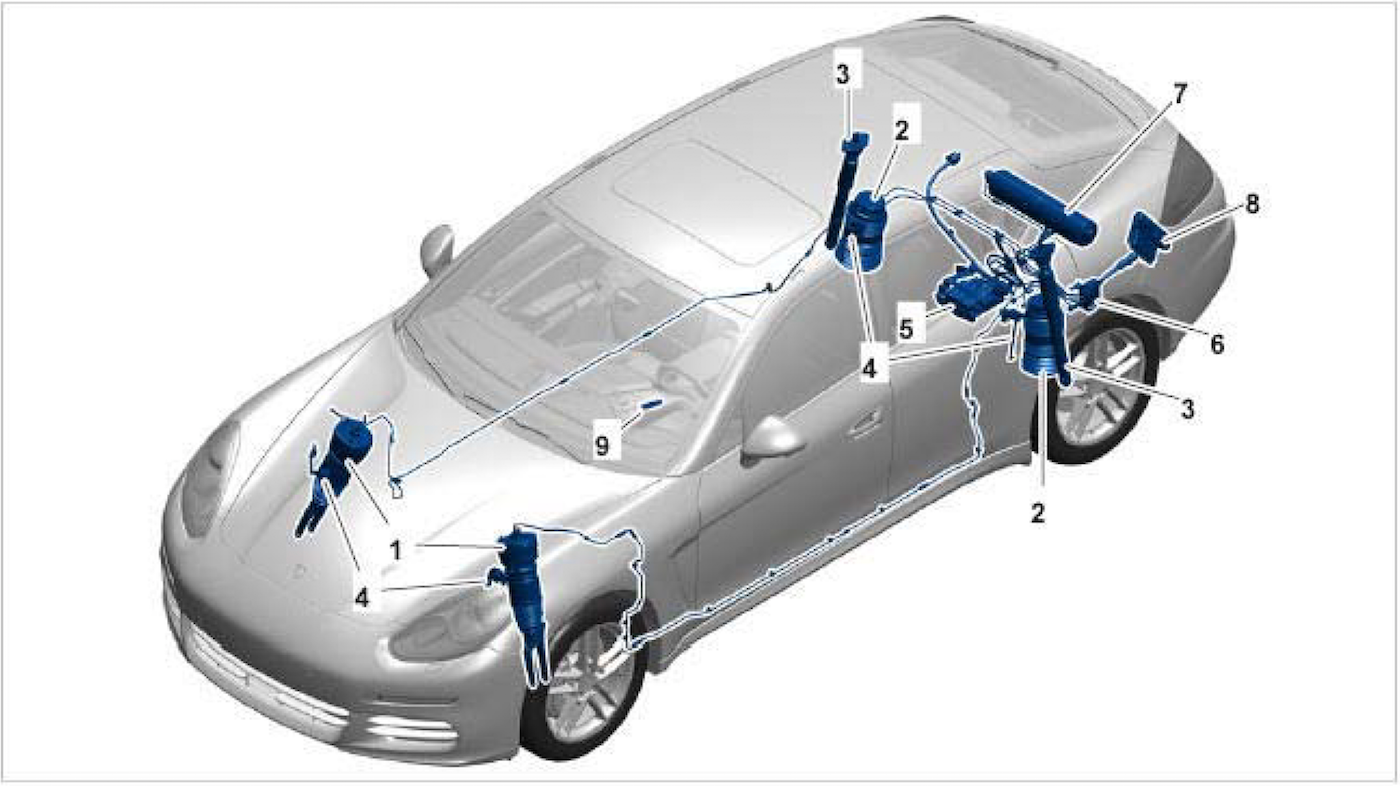

Panamera air suspension is made upwardly of the post-obit pieces, which all must work well, in order for the suspension to work appropriately.
- Air shocks, forepart – air strut for forepart of car
At that place are two front air shocks, which have internal cavities, where compressed air is injected, to raise the car higher, lower it, make shocks stiffer, etc.
These front air shocks have condom bladders, where the air is injected, to achieve desired function. These air cavities are made of rubber material, which, later on few years, will deteriorate, and can start leaking air. The air tin can start leaking from the rubber material (bellows), or can lead out of the top of the stupor, or the upper shock bushing. Leaking from bellows will not exist like shooting fish in a barrel to discover equally they are mostly obstructed past the daze components. Leaking from upper shock bushing tin be observed past spraying soapy h2o onto the top of the stupor. Leak will manifest itself by soapy water making bubbles on top of the shock. The air shocks have 3 connections on the top side of each: Air line/tube (off center, different color for each shock), air shock sensor at center pinnacle of stupor (detects shock expansion/compression with air), and electrical connectedness for valve that lets air in/out of the air stupor (correct near the air line). The air line connects to the air daze via a contumely plumbing equipment, which ensures air tight connection between air line and daze. The sensors and electrical connections are connected to the ECU, so it can tell position of each corner, and suit as necessary, or tin plow electric connections on/off, to control flow of air into/out of stupor. Each air shock has a pressure regulated valve on information technology, making certain that there is some small amount of pressure in the tank at all times, to help forbid damage to the shock internals if it gets compressed difficult (as in after new ane put in and machine is lowered onto new shock). - Air shocks, rear – air strut with spring for rear of the car
These rear air shocks are similar to forepart shocks, simply these reservoirs are separate from the struts that aid support the machine. The air bellows help heighten or lower the motorcar only as the front air shocks. Rear air shocks are assisted by vibration dampers mounted to the side of each shock. Same connections get to the pinnacle of each air shock for rear: Air line (unlike color for each side), electrical connexion for valve in the shock, and sensor that detects if stupor expands/compresses when air is adjusted.
The sensors and electric connections are connected to the ECU, and then it can tell position of each corner, and adjust as necessary, or can turn electric connections on/off, to control flow of air into/out of stupor.
Each air shock has a pressure regulated valve on it, making sure that there is some small corporeality of pressure in the tank at all times, to help foreclose impairment to the stupor internals if it gets compressed hard (as in after new one put in and car is lowered onto new stupor). - Vibration dampers for rear axle
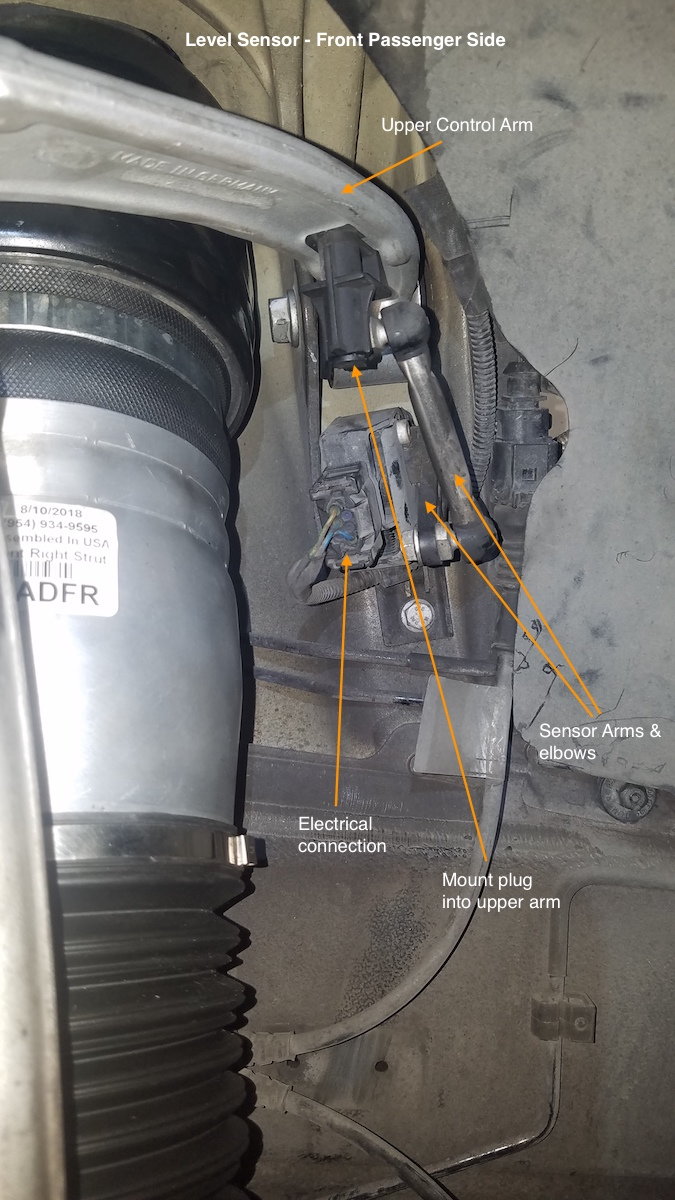
These vibration dampers assistance rear shocks in absorbing chassis movements, making the rear stable while driving. - Level sensors
There are four sensors, each mounted on the upper control arm well-nigh each shock. These sensors detect if the corner of the car was raised or lowered, or if the particular corner of car is outside the 'typical' position (as well high or too depression). These sensors are responsible for mistake messages like 'vehicle is extremely depression', etc. The sensors have one electric connection, and two arms joined with an elbow that allows movement when car goes up or downwards. These sensors are continued to the ECU, and so it tin find each corner position and adjust as necessary. There are additional sensors mounted on top of each air stupor. These sensors detect the aggrandizement/deflation of each shock, and can tell the ECU if the shock how much air is in each stupor (and then ECU knows if the suspension is stiff, loose, etc).- Level Sensor
-
- Level Sensor
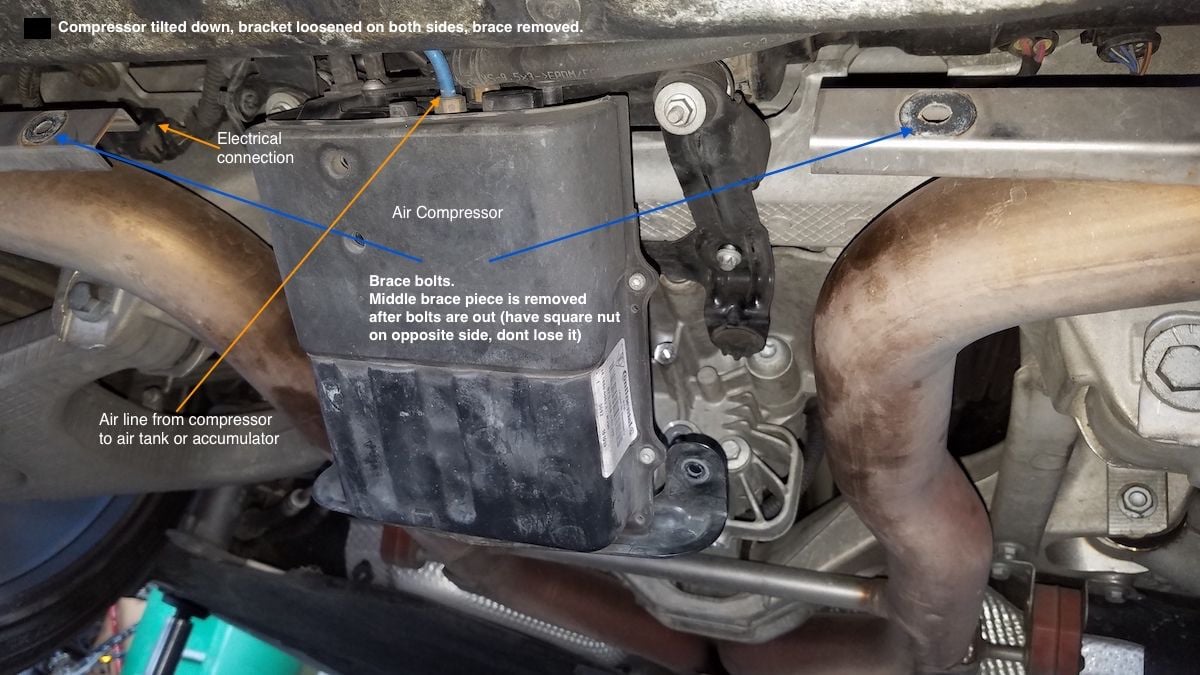
- Air Compressor
Sometimes this is called the air pump. This compressor is located under the car, behind the rear differential, under a protective shield. This compressor compresses air, and feeds it into the air tank. Its sole job is to make sure the air inside the tank, is at predefined pressure, so that the break can be adapted quickly, per pattern. The Air compressor is connected to the ECU via electrical connections. It as well has a filtered line coming out of information technology (see the pigtail in diagram, coming to the left and ending with a circular structure). This round structure is an air filter, making sure clean air goes into compressor from exterior, and so it tin can exist compressed and forced into the air tank. This compressor is as well connected with a color coded air line, to the air tank itself.-
-
- Valve block
Sometimes this is called valve body or valve unit. This valve cake is a group of solenoids, which, when energized (continued to electricity), perform some blazon of piece of work. The work they do is merely to open a valve, allowing compressed air to either go into a shock, out of a daze to be vented out through a dedicated OUT connectedness on the cake itself. This OUT connection is a plastic pipage which ends nether the torso near the bumper. When air is let out of shocks, the compressed air travels out of shocks, through the air lines, into the valve block, and through the OUT port, into the vent line, and is let out of the arrangement (this is the muffled hissing sound yous hear when your car is lowered). Ordinarily, the valve cake is non energized, and all valves are closed (no air is moving through the block). For whatever valve to be open, that valve must get powered from ECU, and corresponding solenoid is energized, opening the paired valve to allow air through. Equally presently equally ECU removed electricity, the valve closes automatically. The valve block has an electrical connection that connects to the ECU. The ECU controls the opening/endmost of each valve/solenoid in the block, when inflating or deflating each daze.-
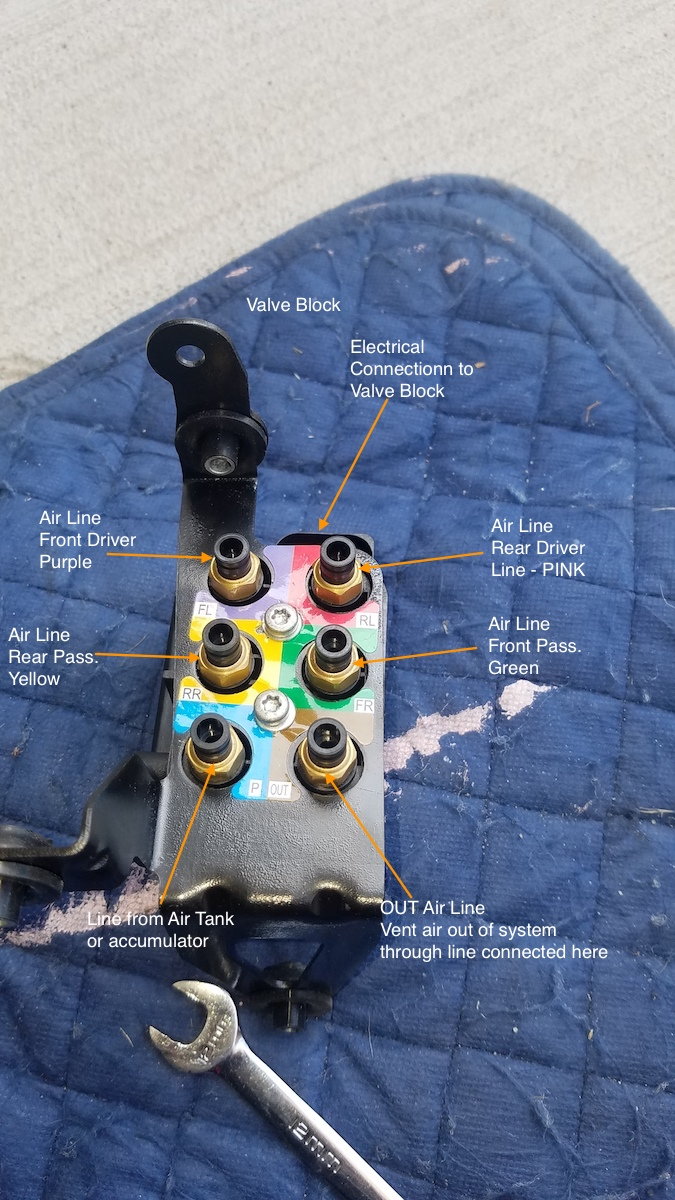

-
- Air tank
Sometimes called the pressure accumulator (because it accumulates or collects compressed air). This is just a metal tank, where compressed air is stored, and then that when necessary, each shock can be inflated quickly. This air tank is connected to the air compressor with one line, and to the valve block with another line. Compressor feeds compressed air to the air tank, and if needed, air tank provides the system with compressed air via connection to valve block. - ECU or Leveling system command unit/PASM
This is the ECU or the leveling system command unit. It is a excursion lath with electronics, that will turn on/off power to pieces of air suspension, volition monitor sensors in the system, monitor position of each corner of machine. This is the brain of the entire system. Issues with ECU, issues with detecting various sensors by the ECU, result in errors such equally the air intermission system failure, etc. This ECU is connected to each shock, each shock sensors (monitor if inflating/deflating), each shock sensor almost upper control arm (control height of the vehicle body), connected to valve block, controlling open/close of each solenoid/valve in the valve body, and is connected to the switches within the machine, the ones yous press if you want to raise the car, make shock stiffer or softer, want to become into sport or sport plus mode, or dorsum into the default comfort mode. - Switches inside the motel to arrange suspension
These are the switches that you utilise to change the configuration of air interruption in your car, higher, lower, condolement, sport, sport plus, etc
Open up OR Closed AIR SUSPENSION Organisation
Now, few things about the organisation, as I learned while debugging, and after speaking to mechanics that work on Panameras.
FSM states this is a closed system. Porsche mechanics would tell yous it is a closed system.
Indy shop mechanics would tell y'all information technology is non a closed system.
I recollect the discrepancy is in the way you view the system itself. The shocks and valve block and air tank compose a closed arrangement. One time pressurized, air remains in shocks and lines. When shocks are lowered though, they let air out of the system, through valve block, through the OUT port on the valve cake, into tubing that vents air under the automobile behind the bumper. Similarly, the compressor draws filtered air from outside, and compresses it for the air tank.
Then you can look at this arrangement as a closed arrangement (shocks, valve block, air tank only), or an open organisation, if y'all include the compressor and the OUT vent line from the valve block.
Whichever way you wait at it, but be aware of how things work and you will be fine.
TYPICAL Arrangement OPERATION
Now, lets become through typical operation of the air suspension organization in the Panamera. This assumes motorcar is working perfectly fine, no issues with suspension.
Yous get into the auto in the morning. Automobile has been standing at that place overnight. Lets assume it got cold over dark. Once you get in, car knows via sensors driver has just gotten into car.
You turn on the ignition and start the machine. Sensors at center of each shock, and nigh upper command artillery, tell the ECU what position the car is in. Automobile knows its last position from night before, when you parked the car.
So if for some reason (common cold atmospheric condition), pressure level in any function of the suspension was decreased, afterward car is started (and all doors closed), the ECU will decide if the air tank needs to be pumped upwardly to proper pressure.
If not, all good to go. If air tank pressure is a little depression, compressor kicks in (relay in body of car will energize, and will close connection to turn on the compressor). The compressor will go on running on a timer and/or the
temperature sensor, and on a pressure level in tank sensor. Once compressor starts, it will shut off if information technology becomes hot, or if the pressure level in air tank reaches desired pressure, or if the compressor runs for more than a couple minutes.
The compressor stops because ECU disconnects electrical connection to the relay in trunk, removing electricity to relay, and therefore removing electrical connection to the power circuit that energizes the compressor.
And so, compressor stops running.
One time air tank is at pressure, ECU has already sensed how loftier your car is, how inflated or deflated your air shocks are. If the machine is too high, air can be let out of the system to return to position dictated past switches in motel.
If car is too depression (got very common cold exterior), the ECU turns on all necessary solenoids/valves in valve block and in shocks, to allow compressed air to travel from loftier compressed area (air tank), to less compressed area (shocks).
Sensors in shocks will tell the ECU when to plough valves off, when proper height or stiffness is reached.
WHAT CAN GO WRONG, HOW TO DETECT & DEAL WITH REPAIR
Now, how does this system fail? Actually, very uncomplicated. You can divide information technology into two categories. Electrical (connections, sensors, ecu, etc), and mechanical (components, connections, lines, etc).
Shocks
If air shocks have leak in them (internally or at meridian of dampers for fronts), air will leak out, causing ECU to detect lower position of shocks, and then making air compressor to piece of work and then the positions can exist corrected.
If the leak is bad plenty, the compressor volition exist asked to turn on mode more than often, causing it to rut upwardly. If plenty estrus gets into the organisation, the air compressor piston/seals, etc tin can get broken, making compressor bad and
requiring either recondition kit with new pistons and seals, or a purchase of another compressor.
If there are leaks in the shocks themselves, the shocks have to exist replaced. There is no way to repair these shocks on your own, since that would require disassembly of each sock, in a manner that cannot exist put dorsum together again.
Special presses are needed to seal the shocks. Then only fashion to set leaking shocks is to buy new ones. You can get OEM brand new ones, or remanufactured ones. Many accept found remanufactured shocks to be good fit, equally price is about 30-40% of new OEM ones,
and they can work for very long time also. Choice dictated by your sense of what you need/prefer to get.
Air lines
Yous can also feel leaks in the air lines themselves. After years of use, a line can crack, causing leaking to occur from the shock itself (valve block is ordinarily all closed, so any compressed air will leak out of the shock).
I think it is difficult to crack air lines, unless work in the area on the motorcar resulted in air lines being twisted, or pinched or forced, in a way to cause a crack. Near the shock connections in engine bay, information technology gets hot, and then I tin can see these connections becoming brittle,
and groovy a chip. In these situations, yous have to buy new air lines, or endeavor to patch a found leak with epoxy, etc.
A skillful way to check if air line is leaking, is to disconnect from daze, and pull vacuum on it, while other terminate is connected to the valve block, and assuming valve cake connectedness or internals are not leaking equally well.
Then, you should see vacuum concord in the line. Otherwise the line has a leak and must be dealt with. Not fixing this will cause low force per unit area in shock all the time, making compressor over piece of work, and beingness broken somewhen.
Level sensors
Sometimes the level sensors near, or on the shocks, volition become defective. This is unremarkably manifested by the system not being able to detect that one or more shocks has been raised or lowered, or if stiffness has changed inside a shock.
If a level sensor goes bad, afterward button is pressed to raise car, you can see car raising, but can come across messages on cluster that the system is faulty. Another instance is irresolute modes to sport or sport plus, and ECU saying
on cluster air suspension system mistake, or inability to enter the mode. Every bit side note, if you cannot enter sport or sport plus style, you lot will usually see other errors on console, forth with limiting automobile power.
Auto thinks something bad going on with intermission when trying to enter sport or sport plus mode, and volition disable these modes based on errors. These boosted errors normally get abroad after result is fixed.
Usually, if level sensors go bad they volition need replacement. Repair is a diy thing and often sensor is junk when cleaved.
Air compressor
Yet some other common failure is the air compressor. This device makes certain the air tank is always at correct pressure level, so that suspension changes can be done quickly (they say under four seconds).
If there is a leak in suspension, the air tank is asked to refill shocks much more often. This results in compressor working much more often to keep the air tank refilled.
Y'all tin can outset your car, close all doors, and stand past passenger side muffler. Listen for low tone humming coming out. That'south the compressor. If you hear it coming on often over 20 minutes of idle, you lot accept suspension problems.
You can troubleshoot compressor issues by codes. Usually suspension system failure can manifest as bad compressor. If you practise non hear compressor kick in at all when y'all printing button to raise suspension, chances are, compressor bad.
If you hear mechanical sounds that sound other than an electrical mattress inflator, you can doubtable compressor.
Sometimes the relay goes bad, which typically will manifest as compressor not kicking on at all, or compressor being on all the fourth dimension (this ane usually results in relay bad).
Any time you lot supervene upon compressor, replace relay besides. This ensures bad relay does not damage new compressor also. New relays have been changed slightly, altering voltage and current they can provide through them, to help compressor.
Valve block
Some other identify common to fail, is the valve block itself. Age tin cause pressure fittings on any of the air lines to valve block, to become leaky. Then yous tin purchase these air fittings and replace in the valve block.
Problem with that is that often the block starts leaking internally too. Near of the time, the entire valve block is replaced. New ane comes with fittings also.
To detect if valve cake connections leak, you spray soapy h2o onto the air lines and fittings, and y'all would come across air bubbling coming from fittings. You cannot exam internal failures unless valve block itself becomes bad.
In this case, some valves volition become stuck, manifesting in 1 corner being stuck depression or high, or perchance all corners stuck in one position, despite using buttons to effort switch to dissimilar configuration.
If only one corner is stuck, maybe two, chances are cake needs replacement.
Air tank / pressure accumulator
Information technology is hard to envision air tank declining, but it is possible something incorrect with the lines makes the tank work bad. Not many things can make tank become bad, except for some puncture making leaks in tank, or lines.
ECU / Leveling system control unit
If the ECU goes bad, the unabridged organisation is no longer being monitored or controlled. This means your tin wont heighten, wont lower, wont change whatever settings for shocks, etc. The brain of the intermission is dead.
Therefore the entire suspension is dead. If nothing happens when y'all press any buttons, and compressor does not kick in, and car does not modify peak, only car has not slammed down (corners do not announced deflated),
information technology is a good sign the ECU is the problem.
Switches inside motel
If you press buttons to change height, modify way, etc, and nada happens, you can suspect the switches in the cabin. Ordinarily 1 or 2 volition non work, but other will. It is unusual for all suspension related buttons to stop working at same time.
If y'all can change modes, but cannot alter stiffness, suspect buttons. Air intermission system failure errors are sometimes caused by buttons (since automobile is not responsive to button changes).
Those would be one of last things I would suspect to go bad though in typical interruption setup debug.
Sometimes, there is a combination of more than one detail going bad. For example, y'all can experience a shock leaking, and while doing debug you accidentally crack an air line.
Or air shock goes bad and slams down, causing a level sensor to become bad as well.
In cases of suspension failures that have no obvious results, you volition have to debug contained systems outset, to make sure you know exactly where the issue is.
PD OF Bug & REPAIR
Offset with shocks that appear to be leaking. Use soap h2o on top of stupor to see if bubbles grade. If yes, you know shocks need replacing. Then, do non remove any air lines. Clamber under car and spray valve cake.
If bubbles form at connections, cake is bad too. Sometimes valve cake is bad internally, and if you cannot determine if adept/bad, dish out the 100 bucks or and so for a new ane.
Unfortunately, only PIWIS2 system has debugging steps built in for air suspension. Other systems can simply read and clear faults. So you lot wont be able to ID valve block bad/practiced unless you lot get wiring diagram,
identify which pins behave the 12V to specific valve in the block, so you lot tin manually energize the valve and cause information technology to open (checking if works ok or not). Y'all tin employ needle to pierce insulation at wire, to ability it with 12V battery.
Air lines should exist connected to valve block if y'all want to decide if they leak. Disconnect line at a shock and employ minor pump to put some vacuum on it. Meet if information technology remains. If it remains, that line is not leaking.
If line cannot hold vacuum, it has a crack. And then you will have to hunt down where the crack is. Normally at either end (seldom does it appear somewhere in middle of line).
If still cant discover line leak, fourth dimension to replace the line (each line is in sections with join connector,
up to y'all how to handle replacement – entire line or a department at a time).
Line leaks would be lesser on priority to cheque unless someone has been playing with removing lines from stupor or from valve block, accidentally cracking one. IF y'all see a crack, you tin can try to epoxy it later wrapping with some adhesive.
Your choice.
Compressors will start making bad sounds before they go bad. There is a piston inside the compressor, with plastic rubber seals, which rub against a sleeve, while air is compressed. If the rubber plastic amercement due to oestrus (running too long), compressor will cease running (volition exist as well hard to move piston and ECU will tell relay to disconnect from power).
Anytime you lot alter compressor, replace relay to make sure bad relay does not break new compressor. Retrieve, a relay is a mechanical way to close/open a circuit with electricity/magnets. One time electricity is added,
magnets force metals to contact, allowing electricity to flow. Once electricity is removed, magnets no longer work, forcing metal contacts away from each other (these contacts are jump loaded, so if magnetic field removed, spring forces contacts apart).
We accept covered air shocks already, just information technology is possible for them to leak where you cannot spray to see the leak. If yous spray elevation of shock and see no leaks, simply then you see car raise the corner, simply to see that corner over again over time, the shock has an internal leak.
Must be replaced, repair non possible without specialty tools and presses.
Past now, I covered components of the air suspension system in the Panamera, what each component does, how it is connected to the balance of the arrangement, how it all works together, forth with some troubleshooting tips.
Hope this will aid others in their course to make some other Panamera drive perfect. Permit me know if you lot take opinions on this info. Thank y'all.
Source: https://www.insanegarage.com/panamera-air-suspension-info-all-you-need-to-know/
Posted by: johnsonbuttere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair Air Suspension Compressor"
Post a Comment